Data management is the key element of cloud applications
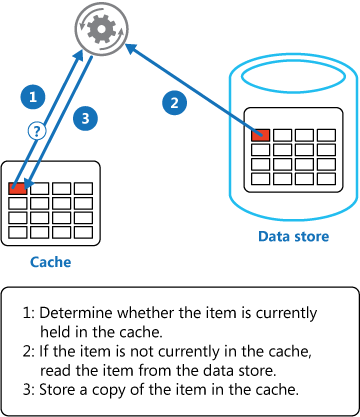
Cache-Aside pattern
Load data on demand into a cache from a data store. This can improve performance and also helps to maintain consistency between data held in the cache and data in the underlying data store.
Command and Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS) pattern
Segregate operations that read data from operations that update data by using separate interfaces. This pattern can maximize performance, scalability, and security; support evolution of the system over time through higher flexibility; and prevent update commands from causing merge conflicts at the domain level.

Event Sourcing pattern
Use an append-only store to record actions taken on data, rather than the current state, and use the store to materialize the domain objects. In complex domains this can avoid synchronizing the data model and the business domain; improve performance, scalability, and responsiveness; provide consistency; and provide audit history to enable compensating actions.

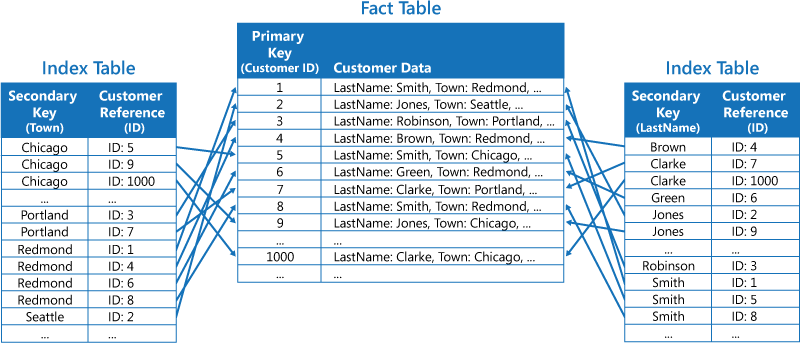
Index Table pattern
Create indexes over the fields in data stores that are frequently referenced by queries. This pattern can improve query performance by allowing applications to more quickly locate the data to retrieve from a data store.
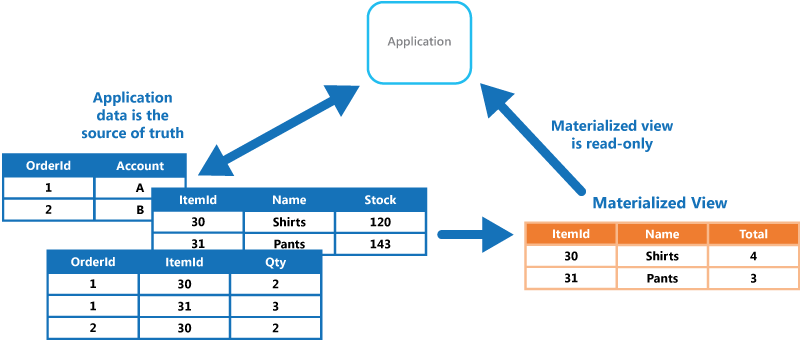
Materialized View pattern
Generate prepopulated views over the data in one or more data stores when the data isn’t ideally formatted for required query operations. This can help support efficient querying and data extraction, and improve application performance.
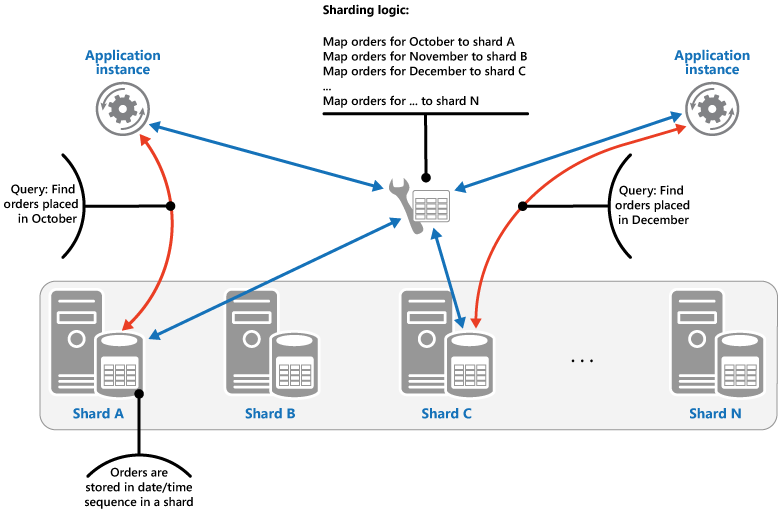
Sharding pattern
Divide a data store into a set of horizontal partitions or shards. This can improve scalability when storing and accessing large volumes of data.
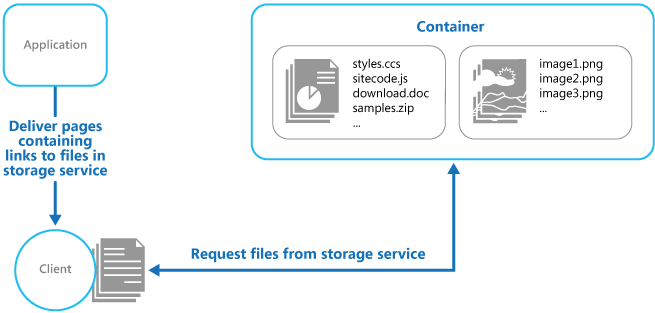
Static Content Hosting pattern
Deploy static content to a cloud-based storage service that can deliver them directly to the client. This can reduce the need for potentially expensive compute instances.
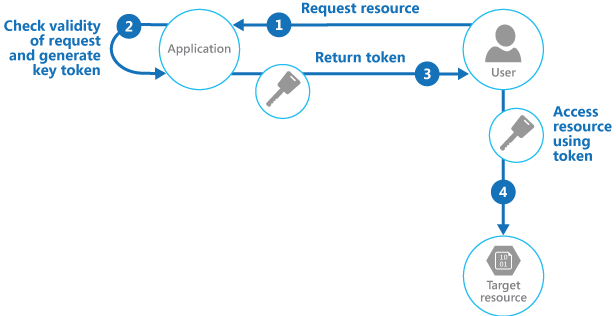
Valet Key pattern
Use a token that provides clients with restricted direct access to a specific resource, in order to offload data transfer from the application. This is particularly useful in applications that use cloud-hosted storage systems or queues, and can minimize cost and maximize scalability and performance.
No comments:
Post a Comment