A cleaner multi-stage continuous deployment on Kubernetes of a Create React App with kustomize, helm and skaffold

(P) Bookmarks.dev - Open source Bookmarks and Codelets Manager for Developers & Co. See our How To guides to help you get started. Share your favorites bookmarks with the community and they might get published on Github -
Most applications depend on external factors that have different values depending on the environment where they are deployed. We mostly use for that environment variables. Guess what? Most of React Apps also have this need. In this blog posts presents a clean(er) way to make a multi-stage deployment of a Create React App on a Kubernetes Cluster. You can use this approach for a seamless integration into your continuous deployment pipeline.
In the beginning it will you show how to set up the React App and then guide you through several deployment possibilities on Kubernetes. You will deploy with native kubectl commands, with helm, with kustomize and in the end use skaffold.
The example app displays the latest public bookmarks published on www.bookmarks.dev. Depending on the environment the app is built for, it will display the environment name in the navigation bar and the header’s color is different.
The source code is available on Github
TLDR;
Create a config.js file where you inject the environment variables in the window object (e.g. window.REACT_APP_API_URL=’https://www.bookmarks.dev/api/public/bookmarks’). Add this file to the public folder of your react application. Dockerize the react application and at Kubernetes deployment time overwrite the config.js file in the container - you can do that with Kubernetes configMaps via native kubectl commands, kustomize or helm.
- TLDR;
- Prerequisites
- React App Setup
- Containerize the application
- Deployment to Kubernetes
- Deploy on Kubernetes with Kustomize
- Deploy on Kubernetes with Helm
- Skaffold
- Conclusion
Prerequisites
To run this application on Kubernetes locally make sure you have Docker Desktop with Kubernetes enabled, this is what I used for testing, or minikube installed. You can also deploy it directly in the cloud if you have an account.
React App Setup
The react application presented in this tutorial is build with create-react-app.
The public folder
You need to add a config.js in the public folder. This will not be processed by webpack. Instead it will be copied into the build folder untouched. To reference the file in the public folder, you need to use the special variable called PUBLIC_URL:
<head>
.....
<title>React App</title>
<script src="%PUBLIC_URL%/config.js"></script>
</head>
The content of the config.js file:
window.REACT_APP_API_URL='https://www.bookmarks.dev/api/public/bookmarks'
window.REACT_APP_ENVIRONMENT='LOCAL'
window.REACT_APP_NAVBAR_COLOR='LightBlue'
Usually the API_URL will point to a different URL depending on the environment, but here it is the same overall.
This was you can set your environment variables on the window object. These are the properties mentioned above. Make sure they are unique, so a good practice is to add the REACT_APP_ prefix as suggested in Adding Custom Environment Variables.
WARNING: Do not store any secrets (such as private API keys) in your React app! Environment variables are embedded into the build, meaning anyone can view them by inspecting your app’s files.
At this point you can run and build the app locally the way you know it:
npm install
npm start
I recommend using nvm to run NodeJS locally
and then access it at http://localhost:3000
Why not use the process.env approach presented in Adding Custom Environment Variables
The runtime of static web-apps is the browser, where you don’t have access process.env, so the values that are dependent on the environment have to be set prior to that, namely at build time. If you do the deployment from your local machine, you can easily control the environment-variables - build the app for the environment you need and then deploy it. Tools like kustomize and skaffold, makes this feel like a breeze in the Kubernetes world as you’ll find out later in the article.
But if you follow a continuous deployment approach, you’d usually have several steps, which form a so called pipeline:
- commit your code to a repository, hosted somewhere like GitHub
- your build system gets notified
- build system compiles the code and runs unit tests
- create image and push it to a registry, such as Docker Hub.
- from there you can deploy the image
The idea is to repeat as little steps as possible for the different environments. With the approach presented in this blog post, it will only be step number five (deployment), where we have environment specific configurations.
Containerize the application
First things first, let’s build a docker container to use for the deployment on Kubernetes. Containerizing the application requires a base image to create an instance of the container.
Create the Dockerfile
The Dockerfile in the project root directory contains the steps needed to build the Docker image:
# build environment
FROM node:12.9.0-alpine as build
WORKDIR /app
ENV PATH /app/node_modules/.bin:$PATH
COPY package.json /app/package.json
RUN npm install --silent
RUN npm config set unsafe-perm true #https://stackoverflow.com/questions/52196518/could-not-get-uid-gid-when-building-node-docker
RUN npm install react-scripts@3.0.1 -g --silent
COPY . /app
RUN npm run build
# production environment
FROM nginx:1.17.3-alpine
COPY --from=build /app/build /usr/share/nginx/html
EXPOSE 80
CMD ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]
It uses a multi-stage build to build the docker image. In the first step you build the React APP on a node alpine image and in the second step you deploy it to an nginx-alpine image.
Build the docker image
To build the docker image run the following command in the project’s root directory:
docker build --tag multi-stage-react-app-example:latest .
At this point you can run the application in docker by issuing the following command:
docker run -p 3001:80 multi-stage-react-app-example:latest
We forward nginx port 80 to 3001. Now you can access the application at http://localhost:3001
Note that the environment is LOCAL, as it uses the “original” config.js file
Push to docker repository
You can also push the image to a docker repository. Here is an example pushing it to the codepediaorg organisation on dockerhub:
docker tag multi-stage-react-app-example codepediaorg/multi-stage-react-app-example:latest
docker push codepediaorg/multi-stage-react-app-example:latest
Deployment to Kubernetes
You can now take a docker container based on the image you’ve created and deploy it to kubernetes.
For that, all you need to do is create a Kubernetes service and deployment:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: service
name: multi-stage-react-app-example
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: multi-stage-react-app-example
type: NodePort
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: service
name: multi-stage-react-app-example
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: multi-stage-react-app-example
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: service
app: multi-stage-react-app-example
spec:
containers:
- name: multi-stage-react-app-example
image: multi-stage-react-app-example:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 80
Kubernetes context and namespace
Before you run any kubectl apply command, it is important to know what context and namespace you are applying your command against.
The easiest way to verify this, is to install kubectx and then issue kubectx to get the current context and kubens for the current namespac. The default namespace is usually called default. In this blog post we operate on the local docker-desktop context and the default namespace.
Now that you know where your kubernetes objects will be applied to, you can add them to a file, like deploy-to-kubernetes.yaml and apply the following the command:
kubectl apply -f deploy-to-kubernetes.yaml
This will create the multi-stage-react-app-example service of type NodePort. You can verify its presence by listing all services
kubeclt get svc
or grep it with kubectl get svc | grep multi-stage-react-app-example
Port forward
To access the application inside the Kubernetes cluster you can use port-forwarding. The command to forward the service created before is
kubectl port-forward svc/multi-stage-react-app-example 3001:80
Note
svcbefore the service name
This commands forwards the local port 3001 to the container port 80 specified in the deployment file. Now you can access the application inside the container at http://localhost:3001, which uses the LOCAL environment.
You might want to hit
Ctrl + Shift + Rto force refresh the website in the browser (Chrome might have cached the old version)
Tear down created Kubernetes objects
To delete the service and deployment created, issue the following command
kubectl delete -f deploy-to-kubernetes.yaml
Make the application deployment aware of the environment
Remember our purpose for continuous delivery pipeline: Make the application “aware” of the environment at deployment to cluster time.
Create a configMap
You start by creating a configMap. We’ll create one for the dev environment from the environment/dev.properties file:
kubectl create configmap multi-stage-react-app-example-config --from-file=config.js=environment/dev.properties
This creates a configMap, which you can then reference by the config.js key and the content are the environment variables.
You can check this by issuing the following kubectl command:
kubectl get configmaps multi-stage-react-app-example-config -o yaml
The result should look something like the following:
apiVersion: v1
data:
config.js: |
window.REACT_APP_API_URL='https://www.bookmarks.dev/api/public/bookmarks'
window.REACT_APP_ENVIRONMENT='DEV'
window.REACT_APP_NAVBAR_COLOR='LightGreen'
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2019-08-25T05:20:17Z"
name: multi-stage-react-app-example-config
namespace: default
resourceVersion: "13382"
selfLink: /api/v1/namespaces/default/configmaps/multi-stage-react-app-example-config
uid: 06664d35-c6f8-11e9-8287-025000000001Å
Mount the configMap in the container
The trick is now to mount the configMap into the container via a volume and overwrite the config.js file with the values from the configMap. Move now the configuration of the service and deployment resources in separate files in the kubernetes folder. The deployment file:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: service
name: multi-stage-react-app-example
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: multi-stage-react-app-example
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: service
app: multi-stage-react-app-example
spec:
containers:
- name: multi-stage-react-app-example
image: multi-stage-react-app-example:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- name: multi-stage-react-app-example-config-volume
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html/config.js
subPath: config.js
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: multi-stage-react-app-example-config-volume
configMap:
name: multi-stage-react-app-example-config
In the volumes section of the specification, define a volume based on the configMap you’ve just created:
volumes:
- name: multi-stage-react-app-example-config-volume
configMap:
name: multi-stage-react-app-example-config
and then mount it in the container in the folder from where nginx delivers its files:
spec:
...
template:
...
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: service
app: multi-stage-react-app-example
spec:
containers:
...
volumeMounts:
- name: multi-stage-react-app-example-config-volume
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html/config.js
subPath: config.js
readOnly: true
Note: you need to use
subpathto only overwrite the config.js file, otherwise the content of the folder is replaced with this file
Deploy on kubernetes “dev” cluster
We will use the same local cluster to test our dev deployment. You apply now kubectl on all the files in the kubernetes directory:
kubectl apply -f kubernetes
Verify that the _config.js file has been replaced by connecting to the pod:
#first export list the pod holding our application
export MY_POD=`kubectl get pods | grep multi-stage-react-app-example | cut -f1 -d ' '`
# connect to shell in alpine image
kubectl exec -it $MY_POD -- /bin/sh
# display content of the config.js file
less /usr/share/nginx/html/config.js
It should contain the variables for the dev environment:
window.REACT_APP_API_URL='https://www.bookmarks.dev/api/public/bookmarks'
window.REACT_APP_ENVIRONMENT='DEV'
window.REACT_APP_NAVBAR_COLOR='LightGreen'
But better see it in action by port forwarding the application. You know now how it goes:
kubectl port-forward svc/multi-stage-react-app-example 3001:80
Navigate to http://localhost:3001 and now you should see the DEV environment on the navigation bar.
In a continuous delivery pipeline you could have two steps:
- create the configMap based on the dev.properties file
- deploy on the target cluster with
kubectlspecified above
Tear down
kubectl delete -f kubernetes
You can take the same approach for other environments, like test or staging.
Deploy on Kubernetes with Kustomize
What if now when deployment into the prod cluster you want to have two pods, instead of one serving the web app. Of course you could modify the deployment.yaml file, specify 2 replicas instead of 1 and deploy. But you can solve this in an elegant matter by using Kustomize, which provides other advantages too.
Kustomize is a standalone tool to customize Kubernetes objects through a kustomization file. Since 1.14, Kubectl also supports the management of Kubernetes objects using a kustomization file, so you don’t necessarily need to extra install it. For this tutorial I suggest you do, as you’ll need it later with Skaffold - on MacOS
brew install kustomize
With Kustomize you define base resources in the so called bases (cross cutting concerns available in environments) and in the overlays the properties that are specific for the different deployments. Here we place kustomize related files in the kustomize folder - tree kustomize:
kustomize/
├── base
│ ├── deployment.yaml
│ ├── kustomization.yaml
│ └── service.yaml
└── overlays
├── dev
│ ├── dev.properties
│ └── kustomization.yaml
├── local
│ ├── kustomization.yaml
│ └── local.properties
└── prod
├── deployment-prod.yaml
├── kustomization.yaml
└── prod.properties
In the base folder we define the service and deployment, because in this case they are overall the same (except the 2 replicas for prod, but we’ll deal with that later).
Deploy to dev cluster with Kustomize
Let’s say we want to deploy to our dev cluster with Kustomize. For that we will use the dev overlays. In the dev kustomization file:
bases:
- ../../base
configMapGenerator:
- name: multi-stage-react-app-example-config
files:
- dev.properties
we point to the bases defined before and use the dev.properties file to generate the configMap.
Before we apply the dev overlay to the cluster we can check what it generates by issuing the following command:
kubectl kustomize kustomize/overlays/dev
Note that the generated configMap name has a suffix (something like -
multi-stage-react-app-example-config-gdgg4f85bt), which is appended by hashing the contents of the file. This ensures that a new ConfigMap is generated when the content is changed. In the deploymant.yaml file the configMap is still referenced bymulti-stage-react-app-example-config, but in the generated Deployment object it has the generated name.
To apply the “dev kustomization” use the following command:
kubectl apply -k kustomize/overlays/dev # <kustomization directory>
Now port forward (kubectl port-forward svc/multi-stage-react-app-example 3001:80) and go to http://localhost:3001
Update an environment variable value
If you for example would like to update the value of an environment variable say, window.REACT_APP_NAVBAR_COLOR='Blue' in the dev.properties file, what you need to do is apply gain the dev overlay:
kubectl apply -k kustomize/overlays/dev
#result similar to the following
configmap/multi-stage-react-app-example-config-dg44f5bkhh created
service/multi-stage-react-app-example unchanged
deployment.apps/multi-stage-react-app-example configured
Note the a new configMap is created and is applied with the deployment. Reload and now the navigation bar is blue.
Tear down
kubectl delete -k kustomize/overlays/dev
Deploy to production with kustomize
As mentioned before, maybe for production you would like to have two replicas delivering the application to achieve high availability. For that you can create an prod overlay that derives from that common base, similar as the dev overlay.
It defines extra an deployment-prod.yaml file:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: multi-stage-react-app-example
spec:
replicas: 2
which is a partial Deployment resource and we reference in the prod kustomization.yaml file under patchesStrategicMerge:
bases:
- ../../base
patchesStrategicMerge:
- deployment-prod.yaml
configMapGenerator:
- name: multi-stage-react-app-example-config
files:
- config.js=prod.properties
You can see it’s being modified by running:
kubectl kustomize kustomize/overlays/prod
and then apply it:
kubectl apply -k kustomize/overlays/prod
If you run kubectl get pods you should now see two entries, something like:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
multi-stage-react-app-example-59c5486dc4-2mjvw 1/1 Running 0 112s
multi-stage-react-app-example-59c5486dc4-s88ms 1/1 Running 0 112s
Now you can port forward and access the application the way you know it
Tear down
kubectl delete -k kustomize/overlays/prod
Deploy on Kubernetes with Helm
What is Helm? According to the documentation:
Helm is a tool that streamlines installing and managing Kubernetes applications. Think of it like apt/yum/homebrew for Kubernetes.
Helm uses the so called Kubernetes charts. Charts are packages of pre-configured Kubernetes resources. If you want to learn more about Helm read the docs, we won’t go into much details here, only punctual where it is needed.
At the moment Helm has a client (helm) and a server (tiller). Tiller runs inside of your Kubernetes cluster, and manages releases (installations) of your charts.
Helm installation
On MacOS you can install the client with homebrew:
brew install kubernetes-helm
For other platforms see Installing the Helm Client.
To install Tiller on your local Kubernetes cluster for testing just call the following command:
helm init
#result should something similar to the following:
Creating /Users/ama/.helm
Creating /Users/ama/.helm/repository
Creating /Users/ama/.helm/repository/cache
Creating /Users/ama/.helm/repository/local
Creating /Users/ama/.helm/plugins
Creating /Users/ama/.helm/starters
Creating /Users/ama/.helm/cache/archive
Creating /Users/ama/.helm/repository/repositories.yaml
Adding stable repo with URL: https://kubernetes-charts.storage.googleapis.com
Adding local repo with URL: http://127.0.0.1:8879/charts
$HELM_HOME has been configured at /Users/ama/.helm.
Tiller (the Helm server-side component) has been installed into your Kubernetes Cluster.
Please note: by default, Tiller is deployed with an insecure 'allow unauthenticated users' policy.
To prevent this, run `helm init` with the --tiller-tls-verify flag.
For more information on securing your installation see: https://docs.helm.sh/using_helm/#securing-your-helm-installation
To check the helm version you can run then the following command:
$ helm version
Client: &version.Version{SemVer:"v2.14.3", GitCommit:"0e7f3b6637f7af8fcfddb3d2941fcc7cbebb0085", GitTreeState:"clean"}
Server: &version.Version{SemVer:"v2.14.3", GitCommit:"0e7f3b6637f7af8fcfddb3d2941fcc7cbebb0085", GitTreeState:"clean"}
Helm setup in project
For this project the helm configuration is present in the helm-chart. This was initially created via the helm create helm-chart command and adjusted for this app’s needs.
Templates
The most important piece of the puzzle is the templates/ directory. This where Helm finds the YAML definitions for your Services, Deployments and other Kubernetes resources. Let’s take a look at the service definition:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name:
helm.sh/chart:
app.kubernetes.io/instance:
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by:
spec:
type:
ports:
- port:
targetPort: http
protocol: TCP
name: http
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name:
app.kubernetes.io/instance:
It looks similar to the one used when installing with Kubectl or Kustomize, only that the values are substituted by Helm at deployment with the ones from Helm-specific objects.
Values
Values provide a way to override template defaults with your own configuration. They are present in the template via the .Values object as seen above.
Values can be set during helm install and helm upgrade operations, either by passing them in directly, or by uploading a values.yaml file.
The configMap
This time we will create the configMap as a Kubernetes object:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: multi-stage-react-app-example-config
annotations:
# https://github.com/helm/helm/blob/master/docs/charts_hooks.md
"helm.sh/hook-delete-policy": "before-hook-creation"
"helm.sh/hook": pre-install, pre-upgrade
data:
config.js:
We use helm hooks to create the configMap before installing or upgrading a helm chart (
"helm.sh/hook": pre-install, pre-upgrade)
The thing is that the resources that a hook creates are not tracked or managed as part of the release. Once Tiller verifies that the hook has reached its ready state, it will leave the hook resource alon - thus you cannot rely upon helm delete to remove the resource. One way to destroy the resource is to add the "helm.sh/hook": pre-install, pre-upgrade annotation to the hook template file.
Deploy to local cluster with helm
Before deploying with helm you might want to examine the chart for possible issues and do a helm lint:
helm lint helm-chart
and execute a dry-run to see the generated resources from the chart
helm install -n local-release helm-chart/ --dry-run --debug
The result should be something like the following:
# result
[debug] Created tunnel using local port: '64528'
[debug] SERVER: "127.0.0.1:64528"
[debug] Original chart version: ""
[debug] CHART PATH: /Users/ama/projects/multi-stage-react-app-example/helm-chart
NAME: local-release
REVISION: 1
RELEASED: Fri Aug 30 06:30:55 2019
CHART: helm-chart-0.1.0
USER-SUPPLIED VALUES:
{}
COMPUTED VALUES:
affinity: {}
configValues: |
window.REACT_APP_API_URL='https://www.bookmarks.dev/api/public/bookmarks'
window.REACT_APP_ENVIRONMENT='LOCAL with helm'
window.REACT_APP_NAVBAR_COLOR='LightBlue'
fullnameOverride: ""
image:
imagePullSecrets: cfcr
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
repository: multi-stage-react-app-example
tag: latest
ingress:
annotations: {}
enabled: false
hosts:
- chart-example.local
paths: []
tls: []
nameOverride: ""
nodeSelector: {}
replicaCount: 1
resources: {}
service:
port: 80
type: NodePort
tolerations: []
HOOKS:
---
# local-release-helm-chart-test-connection
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: "local-release-helm-chart-test-connection"
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: helm-chart
helm.sh/chart: helm-chart-0.1.0
app.kubernetes.io/instance: local-release
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Tiller
annotations:
"helm.sh/hook": test-success
spec:
containers:
- name: wget
image: busybox
command: ['wget']
args: ['local-release-helm-chart:80']
restartPolicy: Never
---
# local-release-multi-stage-react-app-example-config
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: local-release-multi-stage-react-app-example-config
annotations:
# https://github.com/helm/helm/blob/master/docs/charts_hooks.md
"helm.sh/hook-delete-policy": "before-hook-creation"
"helm.sh/hook": pre-install, pre-upgrade
data:
config.js: |
window.REACT_APP_API_URL='https://www.bookmarks.dev/api/public/bookmarks'
window.REACT_APP_ENVIRONMENT='LOCAL with helm'
window.REACT_APP_NAVBAR_COLOR='LightBlue'
MANIFEST:
---
# Source: helm-chart/templates/service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: local-release-helm-chart
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: helm-chart
helm.sh/chart: helm-chart-0.1.0
app.kubernetes.io/instance: local-release
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Tiller
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: http
protocol: TCP
name: http
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: helm-chart
app.kubernetes.io/instance: local-release
---
# Source: helm-chart/templates/deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: local-release-helm-chart
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: helm-chart
helm.sh/chart: helm-chart-0.1.0
app.kubernetes.io/instance: local-release
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Tiller
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: helm-chart
app.kubernetes.io/instance: local-release
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: helm-chart
app.kubernetes.io/instance: local-release
spec:
imagePullSecrets:
- name: cfcr
containers:
- name: helm-chart
image: "multi-stage-react-app-example:latest"
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
protocol: TCP
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /
port: http
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /
port: http
volumeMounts:
- name: multi-stage-react-app-example-config-volume
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html/config.js
subPath: config.js
readOnly: true
resources:
{}
volumes:
- name: multi-stage-react-app-example-config-volume
configMap:
name: local-release-multi-stage-react-app-example-config
Note the names generated for service and deployment
local-release-helm-chart(generated from)andlocal-release-multi-stage-react-app-example-config(generated from `-multi-stage-react-app-example-config)
Now run the installation without the --dry-run flag for the actual installation:
helm install -n local-release helm-chart/
Verify that the helm release is present by listing the helm releases (helm ls):
helm ls
NAME REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION NAMESPACE
local-release 1 Fri Aug 30 06:46:09 2019 DEPLOYED helm-chart-0.1.0 1.0 default
Now port-forward the service (you know how the service it’s called from the dry run above local-release-helm-chart)
kubectl port-forward svc/local-release-helm-chart 3001:80
and access the app at http://localhost:3001 with environment set to “LOCAL with helm”
Tear down helm release
helm delete --purge local-release
Deploy with “dev” values
Now think you’d want to deploy to “dev” cluster. For that you can configure the environment values in a config-dev.yaml file:
configValues: |
window.REACT_APP_API_URL='https://www.bookmarks.dev/api/public/bookmarks'
window.REACT_APP_ENVIRONMENT='DEV'
window.REACT_APP_NAVBAR_COLOR='LightGreen'
which will be used at deployment to override the configValues from the values.yaml file. Use the upsert variation this time, meaning that if the release is not present it will be created:
helm upgrade dev-release ./helm-chart/ --install --force --values helm-chart/config-values/config-dev.yaml
Now port forward kubectl port-forward svc/dev-release-helm-chart 3001:80 and access the app at http://localhost:3001 et voila you’ve deployed the dev environment.
Tear down dev-release
helm delete --purge dev-release
Skaffold
The last thing I want to present is deployment with Skaffold, which is one of my favorite tools.
Let’s see the official definition:
“Skaffold is a command line tool that facilitates continuous development for Kubernetes applications. You can iterate on your application source code locally then deploy to local or remote Kubernetes clusters. Skaffold handles the workflow for building, pushing and deploying your application. It also provides building blocks and describe customizations for a CI/CD pipeline.”
Skaffold features a five-stage workflow:
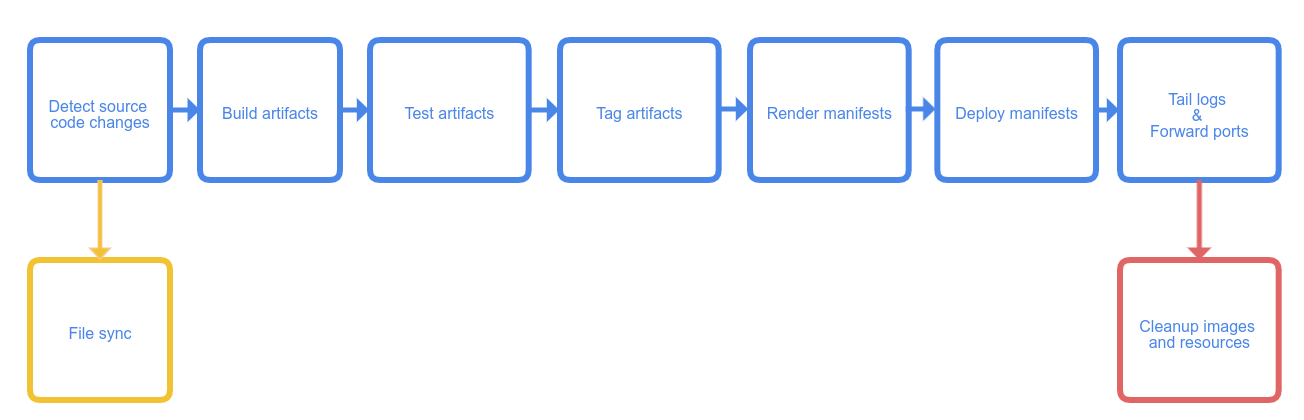
When you start Skaffold, it collects source code in your project and builds artifacts with the tool of your choice; the artifacts, once successfully built, are tagged as you see fit and pushed to the repository you specify. In the end of the workflow, Skaffold also helps you deploy the artifacts to your Kubernetes cluster, once again using the tools you prefer.
Skaffold installation
Before we begin you need to have Skaffold installed. See this link for the installation on your machine. For MacOS is as simple as:
brew install skaffold
Develop with Skaffold
You can configure Skaffold with the Skaffold configuration file skaffold.yaml, which is placed in the root of the project directory:
apiVersion: skaffold/v1beta13
kind: Config
build:
artifacts:
- image: multi-stage-react-app-example
docker:
dockerfile: Dockerfile
deploy:
kustomize:
path: kustomize/overlays/local
portForward:
- resourceType: deployment
resourceName: multi-stage-react-app-example
port: 80
localPort: 3001
profiles:
- name: native-kubernetes
build:
artifacts:
- image: multi-stage-react-app-example
docker:
dockerfile: Dockerfile
deploy:
kubectl:
manifests:
- kubernetes/*
- name: kustomize-prod
deploy:
kustomize:
path: kustomize/overlays/prod
Let’s focus now on the build and deploy parts and ignore the portForward and profiles sections for the moment. We will come back to them later.
The build section is where we describe how the images are build - in our case we build from the dockerfile Dockerfile. For the build it uses the local Docker daemon. See builders for other options to build Docker images.
The deploy section specifies how the images are deployed. In the default configuration here we use kustomize to deploy the local overlay. Skaffold also supports using kubectl and helm. See Deployers for more information.
Skaffold is very flexible - see the skaffold.yaml reference file for other possibilities and explanations.
Local development
Local development means that Skaffold can skip pushing built container images, because the images are already present where they are run. For standard development setups such as docker-desktop, this works out of the box.
Remember you can check the current kubernetes context with
kubectx
# or with standard kubectl command
kubectl config current-context
Mine is docker-desktop.
To run Skaffold you can use the run command (this is the default modus operandi):
skaffold run --tail
in the project root directory.
The --tail option tails the logs in the container.
Now port-forward kubectl port-forward svc/multi-stage-react-app-example 3001:80 and access the app at http://localhost:3001
Tear down local deployment with Skaffold
skaffold delete
Continuous Development Mode
The skaffold run command, standard mode, instructs Skaffold to build and deploy your application exactly once. When you make changes to the source code, you will have to call skaffold run again to build and deploy your application.
Skaffold offers a skaffold dev, continous development mode, which enables the monitoring of the source repository, so that every time you make changes to the source code, Skaffold will build and deploy your application.
In this mode you can also specify the --port-forward, which will port forward your service to a port chosen by Skaffold. You can override the port by specifying it in the portForward section of the skaffold.yaml file.
So now run:
skaffold dev --port-forward
and now you can access the application as usual at http://localhost:3001
In this mode it will also automatically display the containers logs (the
--tailflag fromskaffold run)
This mode is best suited when you have hot redeployment possibilities, but more about that in another post.
Tear down continuous developemtn with Skaffold
You can now use Ctrl+c to tear down the process.
Deploy to other environment with Skaffold profiles
With Skaffold profiles you can define build, test and deployment configurations for different contexts. Different contexts are typically different environments in your app’s lifecycle.
This is the profiles section we mentioned before the skaffold.yaml file
profiles:
- name: native-kubernetes
deploy:
kubectl:
manifests:
- kubernetes/*
- name: kustomize-prod
deploy:
kustomize:
path: kustomize/overlays/prod
The build, test and deploy sections defined in the profile will completely replace the main configuration. The default values are the same in profiles as in the main config. In our case the build part is similar only the deployment parts are different.
Let’s say you want to deploy to the “production” environment. You can call Skaffold with the kustomize-prod profile in the following manner:
skaffold run -p kustomize-prod
Now port-forward kubectl port-forward svc/multi-stage-react-app-example 3001:80 and access the app at http://localhost:3001 You should now see the PROD environment.
Don’t forget you need to change your Kubernetes context (
kubectx), before applying the Skaffold prod profile.
Tear down Skaffold profile
skaffold delete -p kustomize-prod
For more details about Skaffold profiles check out the docs.
Conclusion
It’s been a long ride, but hopefully you learned a few things, like how to deploy a create react app in kubernetes cluster and how to build a basis for a integration in your continuous delivery pipeline. You’ve learn to use Docker, kubernetes api manifests, kustomize, helm charts and skaffold.
I would really appreciate if you had a look at the original www.bookmarks.dev application and give it a try (you might cannot not use it) and star the generated public bookmarks at https://github.com/BookmarksDev/bookmarks.